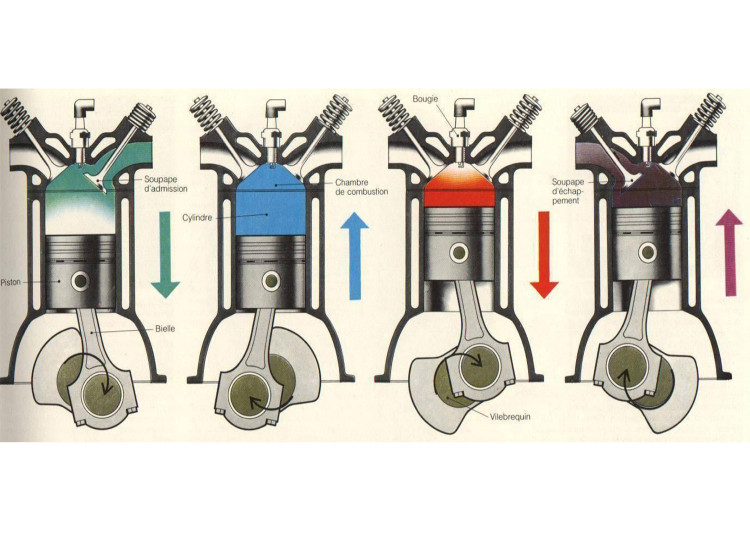
A four-stroke gasoline engine operates according to the following steps:
1. Intake: During this first stage, the piston moves downward in the cylinder, and the intake valve opens. The air-fuel mixture is drawn into the combustion chamber through the open intake valve.
2. Compression: Once the air-fuel mixture is drawn in, the piston moves upward in the cylinder, compressing the mixture. Both the intake and exhaust valves are closed at this stage.
3. Combustion: At the top of the compression stroke, a spark is produced by the spark plug. This ignites the compressed mixture, causing a rapid combustion. The expansion of the combustion gases pushes the piston downward, generating power.
4. Exhaust: After the power stroke, the piston moves upward again, expelling the exhaust gases produced by the combustion out of the combustion chamber through the open exhaust valve. The intake valve remains closed at this stage.
This process repeats in a cyclic manner for each cylinder of the engine, generating the necessary power to propel the vehicle. The intake and exhaust valves open and close at the appropriate times through a synchronized timing system, typically based on a camshaft.
It's important to note that this four-stroke process is a simplification of the actual engine operation, and there may be variations depending on the specific engine design. However, these steps provide a general understanding of how a four-stroke gasoline engine operates.
 Posted 1 year ago
Posted 1 year ago


 Posted 1 year ago
Posted 1 year ago